How to Fix Dynamics 365 Storage Capacity Issues [A Quick Guide]
Feb 26, 2025 Aiswarya Madhu
Managing storage capacity and costs in Microsoft Dynamics 365 is a growing challenge for businesses as data volumes expand and operational demands increase. With database storage priced at $40 per GB and limited default storage allocations, businesses must adopt effective strategies to optimize storage usage while minimizing expenses.
This blog explores the challenges associated with Dynamics 365 storage Capacity and offers actionable tips to help businesses address these issues.
On this Page
Understanding Dynamics 365 Storage Capacity
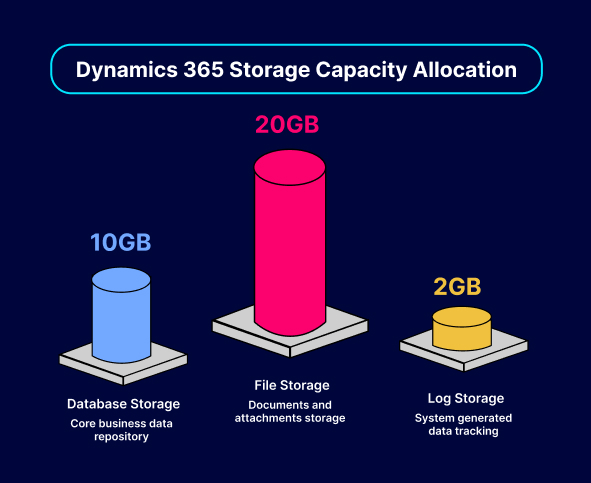
Dynamics 365 offers a flexible storage model designed to handle different types of data. The three primary categories are database storage, file storage, and log storage. Each serves a distinct purpose within the system:
Database Storage
This is where core business data resides, including accounts, contacts, activities, custom entities, and workflows. The default allocation typically starts at 10 GB, with an additional 250 MB per licensed user. If needed, organizations can purchase extra storage to accommodate growing data volumes.
File Storage
File storage is used for documents, attachments, images, and other files associated with records in Dynamics 365. By default, each environment is granted 20 GB of file storage, plus an additional 2 GB per user. This allows businesses to store supporting documents, such as contracts, presentations, and invoices, without consuming valuable database capacity.
Log Storage
Log storage captures system-generated data, including change tracking, auditing, and plugin logs. Each environment receives a fixed 2 GB allocation, which is typically sufficient for tracking system-level activities. Additional log storage can be purchased if extensive auditing and tracking are required.
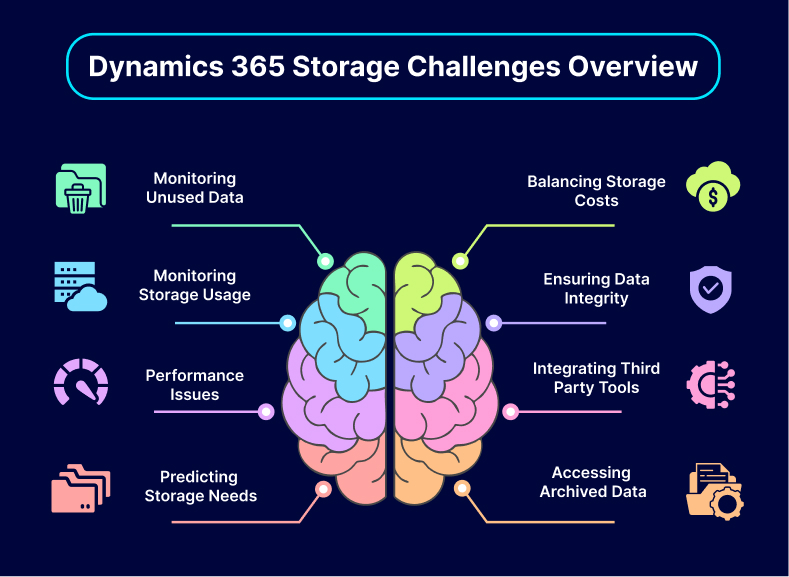
8 Common Dynamics 365 Data Storage Capacity Challenges and Solutions
#Challenge 1: Managing Unused and Redundant Data
Unused and outdated data, such as old cases, opportunities, duplicate records, and audit logs, often build up in Dynamics 365 environments. Over time, this accumulation increases storage consumption and makes it harder for businesses to stay within allocated capacity limits. The real difficulty lies in identifying which records are genuinely no longer needed and removing them without risking data integrity. Organizations that don’t implement a systematic cleanup approach often find their storage costs spiraling and system performance degrading.
Solution:
A structured and ongoing cleanup process is essential. For example, a professional services firm conducted monthly automated checks to identify outdated records, unused opportunities, and audit logs. They used tools designed to detect duplicates and flag records that had been untouched for years. By regularly removing this unnecessary data, they reduced their storage use by 20%, which not only saved costs but also improved database performance and user experience.
#Challenge 2: Balancing Costs While Storing Inactive Data
Businesses frequently need to retain historical records for compliance, auditing, or reference purposes. Keeping these records within Dataverse can be costly, particularly when storage usage exceeds the default allowance.
In one case, a manufacturing company realized that their growing collection of old customer communications and large attachments was driving up their storage expenses significantly. These records were no longer actively used but still had to remain accessible, creating a financial burden.
Solution:
The company decided to move these historical records and attachments to Azure Blob Storage, a cost-effective external storage solution. By offloading inactive data to Azure while ensuring it remained accessible, they cut their storage expenses by more than 80%. This approach allowed them to maintain a lean, cost-efficient primary database without losing access to essential records.
#Challenge 3: Monitoring Storage Usage and Identifying Bottlenecks
Organizations often struggle to pinpoint what is consuming the most storage space. Without detailed insights into usage patterns, it becomes difficult to prioritize cleanup efforts or justify storage upgrades. This lack of visibility can lead to inefficient resource allocation, unexpected costs, and missed opportunities to optimize storage.
Solution:
One retail business leveraged the analytics capabilities within the Power Platform Admin Center. They used built-in dashboards and reporting tools to track storage consumption in real-time, identify which entities or file types were consuming the most space, and determine where they could make the most impactful reductions. This data-driven approach allowed them to streamline their storage footprint and delay the need for costly additional storage.
#Challenge 4: Ensuring Data Integrity During Compression
Compressing large files is a common tactic to save storage space, but it can also introduce risks. Poor compression methods can corrupt files or degrade data quality, which becomes particularly problematic if the compressed data needs to be referenced frequently. A financial services company found that improper compression techniques led to delays and errors in their reporting cycles.
Solution:
To prevent such issues, the company implemented a standardized compression procedure. They tested various compression methods in a controlled environment before applying them to production data. By selecting the most reliable approach and validating results before deployment, they maintained data integrity while significantly reducing the space taken up by large files.
#Challenge 5: Addressing Performance Issues with Large Datasets in Azure SQL
While shifting historical data to Azure SQL can reduce primary storage costs, it often introduces new performance challenges. Some organizations find that querying large datasets stored externally can slow down processes and complicate workflows. For instance, a consulting firm that offloaded years of records experienced slower retrieval times, which frustrated end-users and impacted productivity.
Solution:
The consulting firm took steps to improve performance by partitioning large tables and optimizing their queries. Partitioning allowed their systems to handle data in smaller, more manageable chunks, and optimized queries ensured that even complex searches ran more efficiently. These adjustments helped maintain high performance despite the shift to external storage.
Facing Dynamics 365 Storage Capacity Issues?
We Can Help You Fix Them
#Challenge 6: Integrating and Managing Multiple Third-Party Tools
Many businesses turn to third-party tools for enhanced storage management, but these tools can come with integration challenges. Compatibility issues, additional configuration requirements, and unanticipated maintenance costs can cause operational disruptions. For example, a nonprofit organization adopted several tools without proper testing, leading to workflow interruptions and increased administrative overhead.
Solution:
The nonprofit organization streamlined their approach by rigorously testing potential tools in a staging environment before full deployment. They ultimately chose a single, versatile solution that met all their needs, reducing complexity and improving reliability. This allowed them to manage storage more effectively without burdening their team with multiple toolsets.
#Challenge 7: Predicting Future Storage Needs Accurately
Accurately forecasting storage requirements can be difficult, especially in environments with rapidly growing data volumes. Organizations that underestimate future needs may face unexpected costs and capacity shortages, while overestimating can lead to unnecessary expenses. A healthcare provider, for instance, found themselves repeatedly buying storage at premium rates due to a lack of long-term planning.
Solution:
The healthcare provider began using predictive analytics tools to model their data growth trends. By analyzing historical storage patterns and combining them with projections for future data increases, they established a scalable plan. This allowed them to purchase additional storage at predictable intervals and lower costs, ensuring that they had enough capacity without overpaying.
#Challenge 8: Making Archived Data Accessible
Once large datasets are moved to platforms like Synapse Link, businesses may struggle to retrieve information quickly for audits or operational needs. Without proper indexing or search capabilities, data that should be readily available can become buried, causing delays and inefficiencies. A government agency discovered that the lack of a robust search mechanism in their archive solution slowed compliance checks and frustrated their audit teams.
Solution:
The agency implemented comprehensive indexing within Synapse to ensure that archived records could be located instantly. By setting up logical structures and advanced search capabilities, they made it easier for compliance officers to find what they needed. This streamlined auditing processes and kept their operations running smoothly, even with a reduced storage footprint.
Common Pitfalls in Dynamics 365 Storage Management
Several mistakes can lead to excessive consumption of storage capacity in Dynamics 365, ultimately exhausting available resources. Understanding these common pitfalls can help organizations manage their data more effectively and maintain optimal performance. Below are the most prevalent mistakes users make:
Overusing Activity Tracking
One major mistake that users make is excessively tracking activities, such as emails, phone calls, and notes. While tracking customer interactions is essential for maintaining relationships, the cumulative effect can significantly inflate storage usage.
Organizations often create unnecessary records when logging every interaction without evaluating their relevance. For instance, a marketing team logged every interaction with clients, including unscheduled phone calls and casual emails, resulting in the activity-pointer table being overloaded with millions of records, thereby consuming substantial amounts of storage space.
Retaining Unnecessary Data
Another common error is failing to delete outdated or irrelevant data. Dynamics 365 allows for the retention of historical records, which can become burdensome over time if not managed properly.
Users often neglect to purge old records, such as outdated contact details or irrelevant marketing lists. A sales organization that stored all potential leads from their inception, regardless of conversion status, saw their data storage capacities skyrocket, leading to performance issues and the need for expensive storage upgrades.
Neglecting System Jobs and Audit Logs
Many users overlook the impact of system jobs and audit logs on storage consumption. These logs accumulate quickly, especially in active environments where processes are frequently running.
For example, an organization with numerous automated workflows faced a rapid increase in storage consumption due to suspended workflow jobs not being deleted. These unattended logs took up valuable space, leading to urgent action to reclaim storage and prevent disruption in service.
Utilizing Large Attachments
Storing large attachments within Dynamics 365 can accelerate the exhaustion of storage capacity. Users frequently upload files, including images, documents, and videos, without considering their size or storage implications.
For instance, a project management office integrated numerous large project files directly into Dynamics 365 rather than using external file storage solutions, leading to significant and rapid depletion of storage capacity. This oversight forced them to urgently consider additional storage costs.
Lack of Automation for Data Management
Not utilizing automated tools and features designed for data management is another prevalent oversight. Many users fail to implement bulk deletion jobs or data retention policies.
For example, a company relied heavily on manual processes for data management, leading to the accumulation of obsolete records and attachments. They later found themselves in a predicament where the storage limits were exceeded simply because they had not automated or scheduled regular data cleanup. By contrast, a proactive approach to implementing automated retention would have an immense impact.
Inadequate Data Cleanup Processes
Lastly, users often lack a systematic approach to data cleanup. Organizations should regularly review and clean their data, but many neglect to establish or follow appropriate data governance practices.
For example, a non-profit organization that ran numerous campaigns over the years found itself overwhelmed with outdated campaign records, leads, and donations stored in the system. A failure to periodically assess and clean this legacy data led to storage exhaustion, compounding their operational challenges. Establishing a regular audit process could have prevented these issues.
Conclusion
Managing storage capacity and costs in Dynamics 365 requires a strategic approach. By archiving unused data, optimizing data management practices, leveraging cost-effective storage solutions like Azure SQL, and utilizing advanced tools, businesses can significantly reduce expenses and improve efficiency.
If your organization is facing storage challenges, consider adopting these strategies to manage costs while ensuring your Dynamics 365 system remains scalable and effective.
Need assistance with Dynamics 365 storage capacity optimization? Contact our experts today for personalized solutions to streamline your operations and reduce costs.
Frequently Asked Questions
When your Dataverse storage capacity is running low, you can buy more storage through the Microsoft 365 admin center or by working with a Cloud Solution Provider (CSP) or Microsoft representative. Additional storage is available as capacity add-ons for Database, File, and Log storage in Dynamics 365.
Steps to Purchase Additional Storage:
- Check your current storage usage in the Power Platform admin center.
- Sign in to the Microsoft 365 admin center as a Billing Admin.
- Go to Marketplace and search for "Dataverse capacity".
- Select from the following storage options:
- Dataverse Database Capacity (for entity records and transactions).
- Dataverse File Capacity (for attachments, emails, and notes).
- Dataverse Log Capacity (for system logs and monitoring).
- Choose the required license quantity, subscription length, and billing frequency.
- Click "Buy" to complete the purchase.
- After purchase, the additional storage will be reflected in the Power Platform admin center under Resources > Capacity > Summary.
If purchased via Volume Licensing or CSP, contact your Microsoft partner for assistance.
Microsoft provides Dynamics 365 storage in three categories: database, file, and log storage.
- Database Storage: Starts with 10GB + 250MB per user for Enterprise licenses.
- File Storage: Starts with 20GB + 2GB per user.
- Log Storage: Used for system logs and monitoring.
Additional storage can be purchased on a per-gigabyte basis.
Dynamics 365 Business Central Storage Allocation:
Each Business Central tenant starts with 80GB of shared storage across all environments.
- Premium Users: +3GB per license.
- Essential Users: +2GB per license.
- Device Licenses: +1GB per license.
Additional Storage Pricing:
- 1GB increments: ~$10 per GB/month.
- 100GB package: ~$500 per month (~$5 per GB).
- Discounted 1GB increments: ~$5 per GB/month (if 100GB package is purchased).
Steps to Check Your Storage Usage:
- Go to Power Platform Admin Center.
- Sign in with administrator credentials.
- Navigate to Resources > Capacity.
- Under the Summary tab, check your storage breakdown:
- Database: Stores tables/entities.
- File: Stores attachments and file data.
- Log: Stores system logs and audit information.
- For detailed insights, click Details to view storage consumption per environment and entity.
Yes, Microsoft 365 imposes storage limits based on the subscription type and user role:
- Students: Starting February 2024, Office 365 A1 (free) users will have a 100GB OneDrive storage cap.
- Employees: Most Microsoft 365 business plans include 1TB of OneDrive storage per user.
- Affiliates/Emeriti: Storage allocation depends on institutional policies and assigned licenses.
For specific details, consult your organization's IT administrator.
Recent Posts
QuickBooks to Business Central Migration: A Complete Guide
Mar 02, 2026

AI in Dynamics 365 CE [Where It Actually Saves Money and How to Use It]
Feb 25, 2026

Business Central On-Premises to Online Migration [A Complete Guide]
Feb 20, 2026
Category
Our Expertise
About Author

Aiswarya Madhu
Aiswarya Madhu is an experienced content writer with extensive expertise in Microsoft Dynamics 365 and related Microsoft technologies. With over four years of experience in the technology domain, she has developed a deep understanding of Dynamics 365 applications, licensing, integrations, and their role in driving digital transformation for organizations across industries.
Never Miss News
Want to implement Dynamics 365?
We have plans which will meet your needs, and if not we can tweak them around a bit too!


