AI Agents vs AI Assistants: Understanding the Difference and Why It Matters
Jul 08, 2025 Aiswarya Madhu
Imagine you’re a movie star or perhaps a football star. You probably have:
- An assistant, who takes care of day-to-day tasks at your request, like booking dinner reservations, picking up the dry cleaning, organizing fan mail, and managing your calendar.
- An agent, who works proactively behind the scenes continuously seeking endorsement deals, negotiating contracts, crafting your career trajectory without needing explicit instructions every time.
Your assistant is reactive; they wait for your prompts. Your agent is proactive; they take the initiative to maximize your opportunities and income.
…Can’t think of a better way to explain how these two things work?
Well… AI assistants are like human assistants. They react and complete tasks when prompted. AI agents, in contrast, think ahead, make decisions, and act autonomously toward a goal. Knowing the difference is key to choosing the right AI tools for your business.
AI Assistants vs AI Agents: Side-by-Side Comparison
First, we’ll start with a concise side-by-side comparison to understand the fundamental distinctions between AI assistants and AI agents. Then, we’ll explore their unique strengths, examining core capabilities, real-world use cases, and key deployment considerations to help you determine which approach best aligns with your business objectives and technical requirements.
| Aspect | AI Assistant | AI Agent |
|---|---|---|
| Interaction Style | Reactive; waits for user prompts | Proactive; acts autonomously after goal input |
| Autonomy Level | Low; needs continuous instructions | High; independent decision-making |
| Task Complexity | Simple, well-defined tasks | Complex, multi-step processes |
| Memory | Session-based or none | Persistent and adaptive |
| Tool Integration | Limited to predefined functions | Integrates with multiple external tools |
| Examples | Siri, Alexa, ChatGPT | AutoGPT, autonomous trading bots |
| Typical Use | Scheduling, answering questions, drafting | Workflow automation, optimization, decision-making |
Unsure whether your use case needs an AI assistant or agent?
What Are AI Assistants?
An AI assistant (often called a virtual assistant) is an intelligent application that understands natural language commands—spoken or typed—and executes predefined tasks in response. They are reactive by design: they require a prompt or query to act.
Under the hood, modern AI assistants rely on:
- Foundation models (e.g., OpenAI GPT, Meta’s Llama) to interpret language.
- Natural language processing (NLP) to parse intent, entities, and context.
- APIs and integrations to connect with calendars, email, CRMs, and smart devices.
AI assistants help streamline repetitive workflows, boost productivity, and enhance user experiences in both personal and professional contexts.
Core Capabilities: What Can AI Assistants Do?
AI assistants go well beyond simple prompts and replies. Powered by large language models (LLMs), foundation models, and a suite of integrations, they transform how users interact with data, devices, and workflows. Below is a comprehensive look at their capabilities:
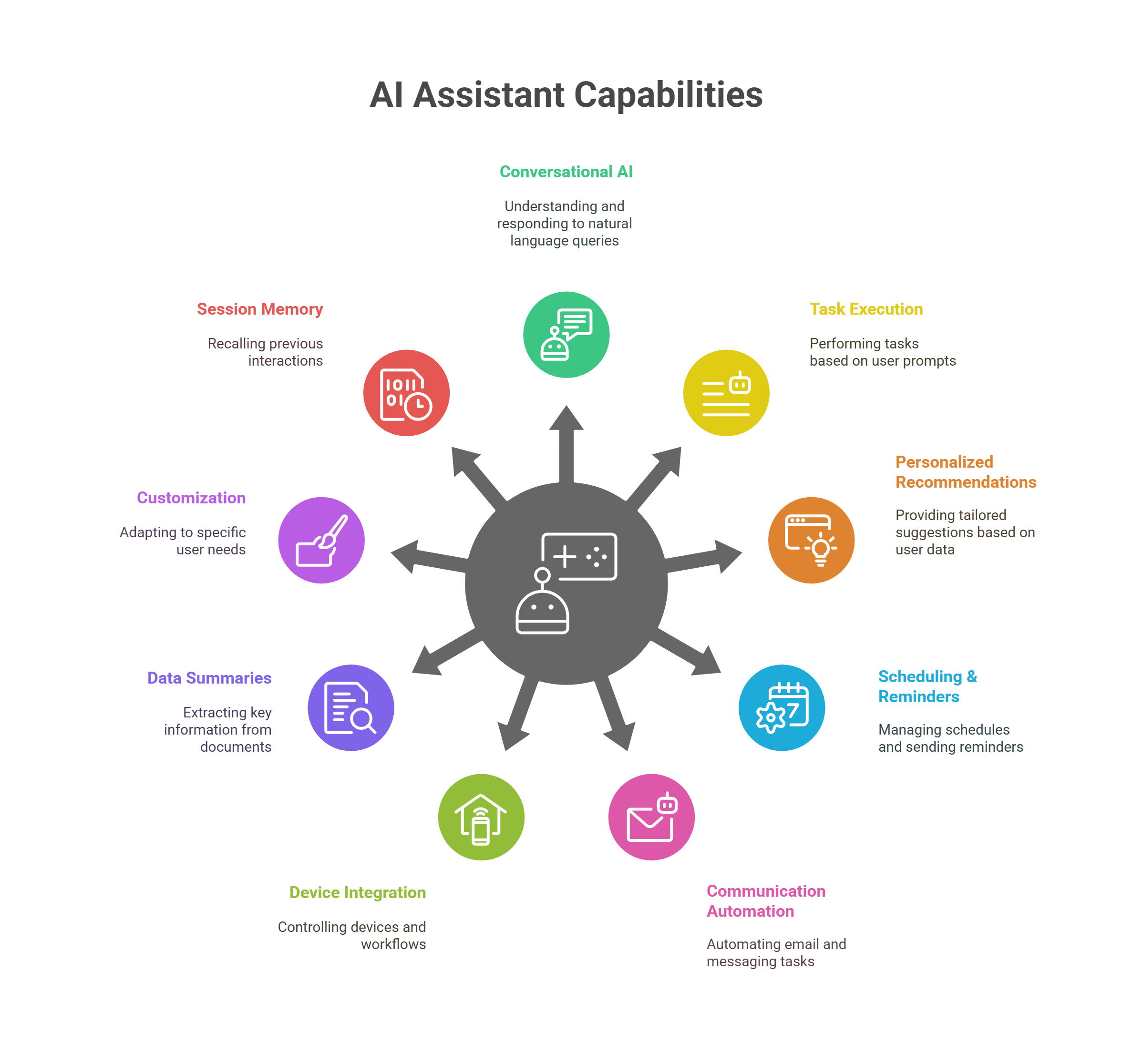
Conversational AI & Natural Language Understanding
Advanced NLP Foundation models (e.g., OpenAI’s GPT, IBM Granite™, Meta Llama) parse nuances in queries—understanding intent, sentiment, and context far beyond keyword matching.
Multimodal Input Some assistants process voice, text, and even images, enabling mixed-media interactions (e.g., “What’s this chart showing?” while uploading a screenshot).
Prompt-Driven Task Execution
Rule-Based to ML-Based Early assistants depended on fixed recipes (“if X, then Y”). Today’s systems leverage ML to generalize across countless user formulations—handling “Book a table for two Friday evening” as effortlessly as “Make me a dinner reservation this Friday.”
Chained Prompts Assistants can manage multi-step requests: “Find me the latest quarterly report, summarize its key findings, then email that summary to the team.”
Personalized Recommendations & Insights
Contextual Suggestions By tapping into your calendar, email, and past behavior, assistants proactively suggest next steps—“Your 3 PM meeting is running over; shall I notify the next attendee?”
Data-Driven Advice In business settings, they can surface relevant metrics—“Sales in your Northeast region up 12 % month-over-month; would you like a slide deck generated?”
Scheduling, Reminders & Calendar Management
Smart Scheduling Beyond setting single events, they negotiate meeting times across time zones, find shared availability, and handle reschedules when conflicts arise.
Persistent Memory They recall your preferences—always block “focus time” after 2 PM; never schedule lunches before 1 PM—and apply those rules automatically.
Email, Messaging & Communication Automation
Drafting & Tone Matching Whether a brief Slack ping or a formal client email, they match your chosen style and language.
Triage & Prioritization By analyzing senders, subjects, and past interactions, assistants flag urgent messages, summarize threads, and even suggest short replies for rapid responses.
Device & Workflow Integration
Smart Home & Office Control Voice commands to adjust lights, thermostats, security systems, or conference-room settings—seamlessly bridging physical and digital environments.
API Orchestration Connectors to CRMs, ERPs, project management tools, and custom internal systems let assistants carry out compound actions like “Pull today’s support tickets, create a summary doc, and attach it to our Slack #ops channel.”
Data Summaries & Document Understanding
Bullet-Point Extraction From PDFs, lengthy reports, or call transcripts, assistants identify key takeaways and generate concise overviews.
Semantic Search Ask questions in natural language (e.g., “Show me all contracts mentioning ‘renewal’ between March and May”)—and retrieve exactly the clauses you need.
Tuning & Customization
Fine-Tuning Models Organizations can provide labeled examples (e.g., specific email formats or domain-specific jargon) so the assistant adapts to in-house terminology and use cases.
Prompt-Tuning & Context Injection Pre-loaded frameworks or “personas” guide the assistant’s behavior—whether acting as a legal compliance aide or a creative marketing brainstorm partner.
Session Memory & Short-Term Context
Conversational Continuity Within a session, assistants recall earlier user inputs—“As I mentioned this morning, could you follow up on that invoice?”—maintaining coherence without repeated restatement.
Context Windows Modern LLMs handle thousands of tokens, letting assistants analyze entire project briefs or long email chains in one go.
Limitations to Keep in Mind
Even the most advanced AI assistants have boundaries:
Dependence on Prompts They won’t act until you ask—no autonomous goal pursuit.
Memory Constraints Unless specifically configured, they may not retain details beyond a session or require manual “memory bookmarks.”
Accuracy & Hallucinations Without rigorous validation, generative responses can introduce errors. Users should always review critical outputs.
Tool Boundaries Assistants can only interact with services they’ve been integrated with; custom connectors may be needed for proprietary systems.
Examples of AI Assistants
Below are five industry-defining AI assistants, each showcasing unique strengths and innovations. Understanding their differentiators can help you select the right “voice” for your organization’s needs.
| Assistant | Core Strength | Unique Differentiator |
|---|---|---|
| Amazon Alexa | Voice-first home & commerce | Alexa Skills marketplace: 100,000+ third-party integrations—from smart lights to shopping carts—enabling rapid extension into new domains. |
| Apple Siri | Seamless device synergy & privacy | On-device processing for many tasks, minimizing data sent to the cloud and strengthening user privacy. |
| Google Assistant | Information recall & cross-platform context | Leverages Google’s search index plus continued conversation across Android, Wear OS, and Nest devices. |
| Windows Copilot | Enterprise productivity integration | Integrated across Microsoft 365, Copilot assists with drafting emails, summarizing documents, analyzing spreadsheets, and managing Teams meetings. |
| Samsung Bixby | Visual + voice command fusion | Bixby Vision: interprets images in real time (e.g., product) |
How to Build Your AI Assistant: A Step-by-Step Guide
Clarify Your Objectives
- Identify the primary tasks your assistant must handle (e.g., scheduling calls, answering FAQs, or gathering customer data).
- Define success metrics—response accuracy, time saved by users, or first-contact resolution rate.
Map the Conversation Flow
- Sketch the typical user journey: what the user says first, how the assistant gathers missing details, and how it concludes.
- Break that journey into discrete “actions” or steps (e.g., ask for an account number, verify identity, provide balance).
Choose Your Platform and Tools
- Select an AI-assistant builder—commercial (Dialogflow, Rasa, Microsoft Bot Framework) or open source—based on your integration needs.
- Ensure it supports natural-language processing, multi-step actions, and API/webhook integrations.
Create and Configure Actions
- Set up AI-guided actions to handle open-ended queries using a foundation model.
- Build skill-based actions for common workflows (login, order status) that invoke your existing services.
- Define custom actions for any unique processes, each with its own prompts, user-response rules, and follow-up logic.
Integrate with Back-End Systems
- Connect to CRM, ERP, ticketing systems, or databases via secure APIs so the assistant can fetch or update data in real time.
- Store user inputs in session variables to maintain context throughout the conversation.
Test, Iterate, and Refine
- Run through every scenario—happy paths and edge cases alike—to ensure prompts and validations behave correctly.
- Adjust conditional steps so the assistant branches appropriately (e.g., asking for confirmation if a high-value transaction is detected).
Deploy and Monitor Performance
- Launch your assistant on the desired channels—website chat widget, messaging apps, or voice platforms.
- Track key metrics such as user satisfaction, completion rate, and error trends.
- Schedule regular reviews to fine-tune language models, update built-in knowledge, and expand capabilities.
Need help implementing AI Assistants or Agents?
AI Assistant Security: Risks to Watch and Safeguards to Implement
Skill Hijacking and Trojan Integrations
Malicious skills or actions can mimic legitimate ones, leading users to install or invoke a rogue extension that steals data or executes unauthorized commands. To guard against this, vet every third-party skill, require code signing, and restrict skill publication to trusted marketplaces.
API and Data Source Tampering
Since assistants pull data from external APIs for tasks like account lookups or calendar events, a compromised endpoint can feed false or malicious information back to the user. Secure your integrations by enforcing strict OAuth scopes, setting rate limits, validating all inputs and outputs, and conducting regular security audits on every connected service.
Semantic Content Poisoning
Voice or text assistants that search the web for answers can be misled by poisoned content—web pages that rank highly for specific queries yet deliver misleading or harmful instructions. Mitigate this risk by whitelisting reputable data sources, applying sanity checks on retrieved content, and caching verified responses for high-impact queries.
Privacy and Personal Data Exposure
AI assistants often handle sensitive personal information such as names, addresses, health details, and payment credentials. Ensure that data at rest and data in transit are encrypted, apply strict data retention policies, and provide users with clear controls to view, export, or delete their stored interactions.
Key Best Practices
- Enforce multi-factor authentication for any task that involves personal or financial data.
- Log and monitor all assistant interactions with anomaly detection to flag unusual patterns.
- Conduct regular penetration tests on the assistant’s conversational interfaces and back-end APIs.
What Are AI Agents?
An AI agent is an autonomous software system that pursues a clearly defined objective by planning, reasoning, executing tasks and then refining its approach—all without ongoing human intervention. Once given a goal, it decomposes that goal into smaller subtasks, assembles the necessary tools or data sources, makes decisions about which actions to take and when, and then learns from each outcome to improve future performance.
Key Features:
- Proactive initiative: Rather than waiting for each user prompt, an AI agent begins work as soon as its objective is set and continually drives progress toward that target.
- Goal-driven workflows: It transforms high-level aims into sequenced tasks, mapping dependencies and orchestrating complex processes.
- Dynamic autonomy: An AI agent selects which APIs, models or services to call, adapts its plan when conditions shift and self-optimizes through feedback loops.
Core Capabilities of AI Agents
AI agents combine sophisticated algorithms, learning mechanisms, and external integrations to operate autonomously and intelligently. Below are the core capabilities that enable them to deliver transformative value across industries.
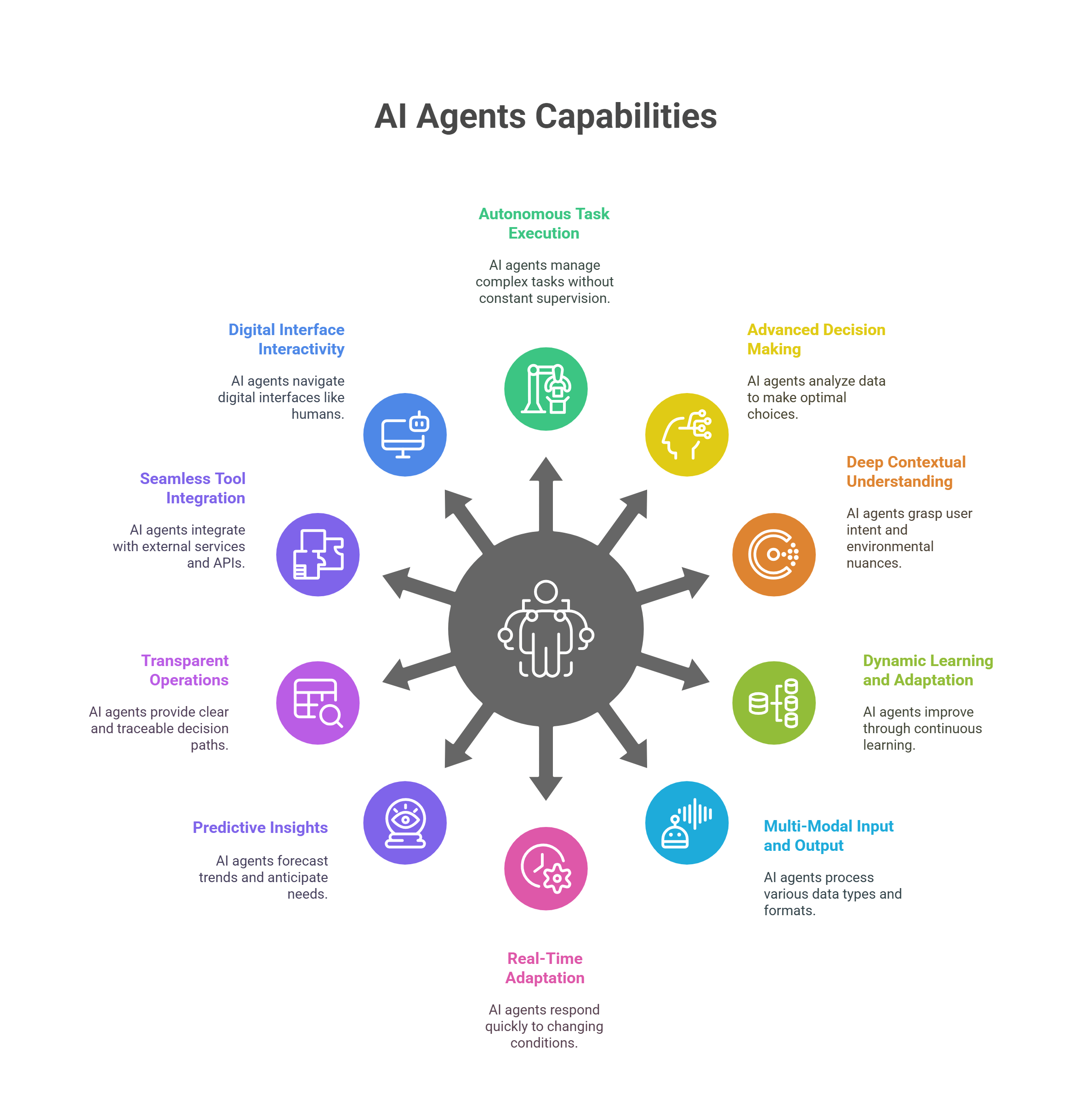
Autonomous Task Execution
AI agents plan and carry out complex workflows without constant supervision. They can break high-level objectives into a sequence of subtasks, monitor progress, recover from errors, and optimize their own performance over time. This autonomy ensures projects advance even when human oversight is minimal.
Advanced Decision Making
By analyzing multiple streams of data in real time, AI agents weigh competing options and choose the best path forward. They evaluate trade-offs between time, cost, risk, and other constraints just as an expert would, then adjust their decisions dynamically as new information emerges.
Deep Contextual Understanding
Moving beyond literal instructions, AI agents grasp user intent and environmental nuances. They maintain conversational context, recall relevant background details, and apply domain-specific knowledge to interact more naturally and make more relevant recommendations.
Dynamic Learning and Adaptation
Every interaction becomes an opportunity to improve. AI agents detect patterns in successes and mistakes, refine their models on the fly, and adjust strategies to perform better in future scenarios. This continuous learning loop drives steadily increasing accuracy and efficiency.
Multi-Modal Input and Output
Text, voice, images, numerical data and more can all be processed by AI agents. They interpret photos or video frames, transcribe and synthesize speech, extract insights from spreadsheets, and generate responses in the most suitable format for each user or system.
Real-Time Adaptation
When conditions shift unexpectedly, AI agents immediately reprioritize tasks, reroute workflows, and reallocate resources. This agility allows them to respond to sudden changes such as an urgent customer request or a spike in data traffic—without missing a beat.
Predictive Insights
By mining historical and current data, AI agents forecast trends, anticipate user needs, and flag potential issues before they arise. They can recommend preventative measures, optimize inventories, or suggest personalized next steps, turning reactive processes into proactive strategies.
Transparent Operations
Trust requires clarity. AI agents log their decision pathways, expose key factors behind each action, and provide traceable activity records. Explainable outputs and performance metrics give users and auditors confidence in their reliability and fairness.
Seamless Tool Integration
AI agents call on external services and APIs as needed—from database queries and analytics platforms to code execution environments and web-scraping tools. This plug-and-play capability vastly expands their operational reach and enables them to tackle tasks across any connected system.
Digital Interface Interactivity
Whether driving a web application, orchestrating backend processes, or manipulating files, AI agents can navigate multiple digital interfaces just like a human user. Their cross-platform compatibility ensures they fit smoothly into existing IT ecosystems and workflows.
Examples of AI Agents
| AI Agent | Core Functionality | Stand-Out Features |
|---|---|---|
| AutoGPT | Fully autonomous goal-driven agent built on GPT-4/3.5 |
|
| BabyAGI | Task manager that creates, prioritizes, and completes jobs |
|
| Abacus.ai | Enterprise-grade agent platform |
|
| AgentGPT | Browser-based agent creator and launcher |
|
| KwaiAgents | Information-seeking agents powered by LLMs |
|
How to Build an AI Agent
Define the Goal
- Identify the specific problem or task your agent must solve
- Determine the type of input (text, voice, images) and the desired output
- Choose the level of autonomy required (from simple rule execution to continuous learning)
Select Tools and Frameworks
- Pick a programming language that suits your needs (Python for rapid prototyping or JavaScript for browser-based agents)
- Choose AI libraries for natural language processing, machine learning or computer vision (e.g., Hugging Face Transformers, TensorFlow, or OpenCV)
- Decide between pre-trained models (GPT, BERT) and custom training based on your data
Gather and Prepare Data
- Collect representative samples of user inputs: chat transcripts, support tickets, or sensor logs
- Clean and normalize data to remove errors and ensure consistency
- Label your data with intents, categories, or outcomes so the agent can learn context
Design the Architecture
- Map out how the agent processes inputs, plans actions, and generates responses
- Define components for perception, decision-making, action execution, and memory
- Plan integrations with external systems, APIs, databases, or UIs
Train and Fine-Tune
- Split data into training and validation sets to measure performance
- Configure hyperparameters such as learning rate, batch size, and number of epochs
- Monitor metrics like accuracy, loss, or response quality and adjust settings to prevent overfitting
Test in Realistic Scenarios
- Run simulated conversations or tasks to verify correctness and reliability
- Conduct user trials to gather feedback on clarity, speed, and usefulness
- Use A/B comparisons to refine dialogue flows or decision logic
Deploy and Monitor
- Integrate your agent into its production environment (website, app, or device)
- Track key indicators: response time, resolution rate, and user satisfaction
- Continuously update the model with new interactions and retrain as needed to maintain accuracy
AI Agent Security: Risks to Watch and Safeguards to Implement
Privilege Escalation via Agent Identities
Autonomous agents acting on behalf of users or systems may accumulate permissions beyond their intended scope. A rogue or compromised agent can exploit these privileges to access sensitive resources or reconfigure infrastructure. Enforce the principle of least privilege by assigning narrowly scoped credentials, require short-lived tokens, and routinely audit agent identities and role assignments.
Prompt Injection and Task Manipulation
Attackers can craft malicious inputs that alter an agent’s task flow or bypass safety checks, causing it to perform unintended actions—such as deleting files or leaking data. Sanitize and validate all incoming prompts, implement strict schema enforcement for task definitions, and insert intent-validation steps before critical sub-tasks execute.
Untrusted Tool or API Invocation
Agents often leverage external tools, scripts, or APIs to complete complex workflows. A compromised tool or endpoint can become a backdoor into your environment, allowing data exfiltration or lateral movement. Isolate tool execution in sandboxed environments, require code signing for all agent-invoked modules, and monitor API calls against predefined allowlists and rate limits.
Model and Data Poisoning
If an agent’s knowledge base, memory store, or model weights are tampered with—either by malicious training data or corrupted retrieval indices—the agent may learn harmful behaviors or disseminate false information. Protect model artifacts and data stores with integrity checks such as cryptographic hashes, enable versioning on all datasets, and restrict write access to a small, vetted team of maintainers.
Chained Agent Exploits
Multi-agent systems coordinating across tasks can inadvertently propagate a compromise from one agent to the next. An attacker who hijacks a lower-privilege helper agent can leverage it to pivot toward higher-privilege orchestrator agents. Segment agent networks by function, enforce mutual authentication between agents, and apply network micro segmentation to limit agent-to-agent communication.
Sensitive Data Leakage in Logs and Memory
Agents record interactions, decisions, and environmental states in logs or memory buffers. Unrestricted log access or overly verbose debugging can expose personal data, credentials, or proprietary algorithms. Mask or redact PII before logging, encrypt logs at rest and in transit, and adopt strict retention policies that automatically purge sensitive records.
Key Best Practices
- Assign each agent a minimal permission set and rotate credentials automatically
- Validate and sanitize every incoming prompt against a defined schema
- Sandbox and code-sign all external tools and plugins invoked by agents
- Implement integrity verification for models, memory stores, and knowledge bases
- Enforce mutual authentication and network segmentation in multi-agent setups
- Mask or redact sensitive data in logs and limit log retention to approved intervals
- Require human approval for high-risk or irreversible agent actions
- Continuously monitor agent behavior and trigger alerts on anomalous patterns
When to Use AI Assistants and When to Use AI Agents?
This section breaks down when a simple assistant will do the job—and when you’ll need a more advanced agent to handle the work.
Use AI Assistants When:
- Tasks are simple, repetitive, and well-defined.
- You want real-time, interactive support to augment human efforts.
- Transparency and human control over every step are required.
Example: Customer support chatbots answering FAQs or a personal assistant drafting emails.
Use AI Agents When:
- Tasks require complex planning, autonomous execution, and decision-making.
- You want end-to-end automation without constant human supervision.
- The workflow benefits from adaptability and integration across multiple systems.
Example: A supply chain agent dynamically rerouting deliveries based on traffic and inventory data.
Conclusion
Choosing between an AI assistant or an AI agent comes down to the level of autonomy, complexity, and integration your use case demands. AI assistants excel at reactive, user-driven tasks that benefit from real-time interaction and human oversight, while AI agents shine in proactive, goal-oriented workflows that require end-to-end automation and adaptive decision-making. By aligning your needs with each technology’s strengths, you can deploy the right solution to elevate efficiency, accuracy, and innovation across your organization.
Recent Posts

Business Central On-Premises to Online Migration [A Complete Guide]
Feb 20, 2026

15+ Years In [From Dynamics 365 Expertise to Enterprise Solutions Delivery]
Jan 20, 2026

Power BI SharePoint Integration Guide
Jan 09, 2026
Category
Our Expertise
About Author

Aiswarya Madhu
Aiswarya Madhu is an experienced content writer with extensive expertise in Microsoft Dynamics 365 and related Microsoft technologies. With over four years of experience in the technology domain, she has developed a deep understanding of Dynamics 365 applications, licensing, integrations, and their role in driving digital transformation for organizations across industries.
Never Miss News
Want to implement Dynamics 365?
We have plans which will meet your needs, and if not we can tweak them around a bit too!


